Video surveillance has shifted dramatically from analog systems simply recording evidence to intelligent cameras that can see, reason and alert in real time. In healthcare – particularly across hospital networks and senior care facilities – safety, quality of care and operational efficiency depend on effectively monitoring patients, staff and environments. The combination of artificial intelligence (AI) and computer vision is transforming camera monitoring from passive observation to proactive, predictive protection. This blog traces the history of surveillance technology, reviews the current landscape of AI camera monitoring in healthcare and senior living, and looks ahead at how AI will shape the next generation of care.
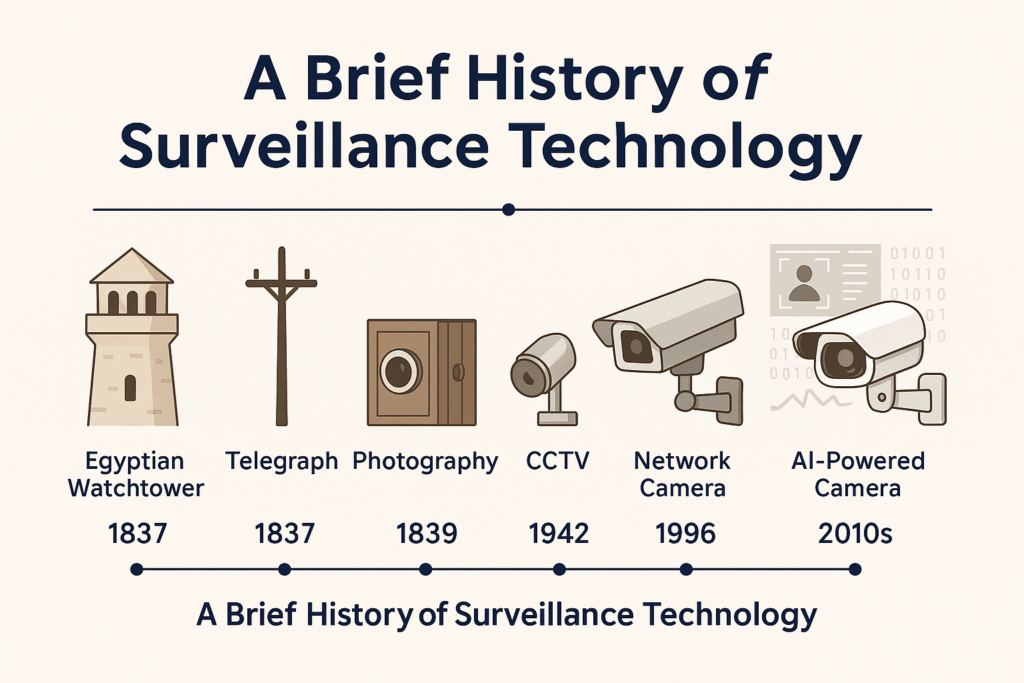
Modern AI camera monitoring has deep roots. Historically, civilizations used physical structures such as Egyptian watchtowers to safeguard temples. The Industrial Revolution laid the foundation for electronic surveillance: the telegraph (1837) enabled long‑distance transmission of signals; photography (1839) made it possible to capture images; Edison’s electric light (1879) allowed round‑the‑clock visibility; and the motion‑picture camera (1891) paved the way for video recording.
Closed‑circuit television (CCTV) emerged during World War II; German researchers developed the first CCTV system in 1942 to monitor bomber runways. By 1949 U.S. contractors were commercializing CCTV for industry, and police departments began installing cameras to monitor public streets in the 1960s. The 1970s brought VCR technology, making it possible to record and play back footage, and the 1980s saw widespread adoption of CCTV for general security. Innovations accelerated in the 1990s and 2000s: network cameras (Axis Communications introduced the first in 1996) enabled remote access, multiplexing allowed multiple cameras to share a single recorder, and IP‑based video recorders and cloud storage reduced hardware costs.
By the 2010s, artificial intelligence and deep learning began powering video analytics. AI algorithms can identify objects, track people and detect anomalies in real time. This shift from passive recording to active monitoring set the stage for camera systems that enhance safety, operational efficiency and quality of care across industries.
Modern hospitals have thousands of cameras. At HonorHealth in Arizona, security teams maintain about 2,000 cameras covering entrances, exits, pharmacies and sensitive areas. AI systems monitor these feeds and trigger alarms when a patient’s actions cause concern; for example, they flag violent behaviour or unusual movement in emergency rooms. AI assistance sorts through footage so staff don’t have to watch each camera, and the system can spot irregular events, such as a visitor wearing a thick coat on a hot day or an unattended wheelchair that might cause an accident. Alerts enable staff to clean spills or relocate obstacles before accidents occur.
Hospitals are moving from reactive to proactive monitoring by integrating predictive analytics into camera systems. HonorHealth plans to build a real‑time operations centre where analytics and computer‑vision algorithms help security teams spot threats and mobilize resources quickly. This shift demonstrates how AI cameras can become central to hospital command centres.
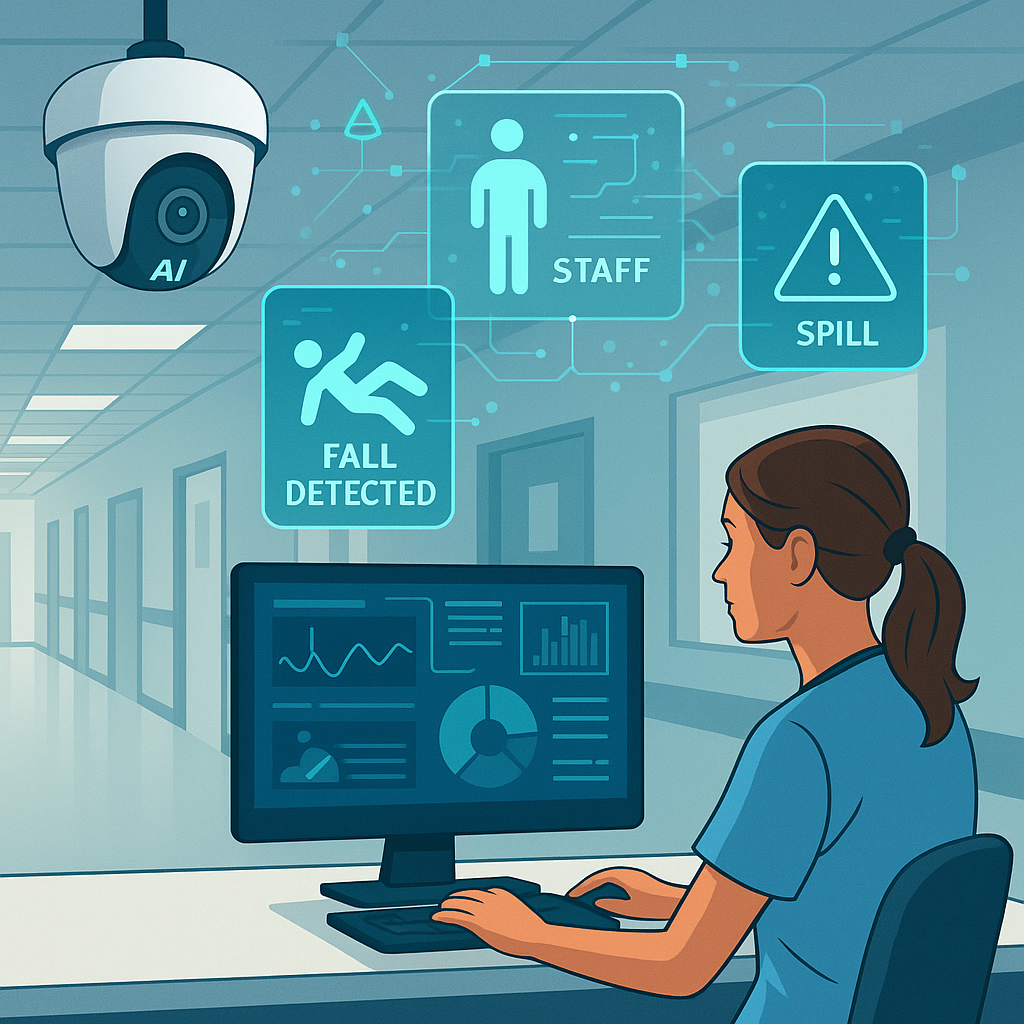

Some health systems are testing AI‑supported cameras directly in patient rooms. In January 2025 UC San Diego Health confirmed it is exploring AI cameras capable of detecting falls and pressure injuries before they occur. Officials emphasized that if implemented, the program would prioritize patient safety, data privacy and compliance, and the video stream would not be stored long‑term. Questions about privacy and consent remain, but such trials illustrate the growing interest in AI vision for bedside care.
Academic research shows how AI cameras can continuously monitor high‑risk patients. LookDeep Health deployed a platform across 11 hospitals that provides real‑time monitoring of high‑risk fall patients. The system captures video at one frame per second, detects objects (patient, staff, bed, chair), classifies roles and estimates motion; it then uses logical predictions to determine whether a patient is alone or supervised. All faces are blurred and identifiable data is removed in compliance with HIPAA. Preliminary results show that continuous monitoring can detect extended periods of patient isolation or movement patterns that indicate a risk of falls or pressure injuries; real‑time alerts allow staff to intervene and prevent harm . Moreover, data from the system helps hospitals allocate staffing resources and track recovery progress.
Falls are a leading cause of injury among seniors. Kami Home markets an AI‑based fall‑detection camera that sends alerts quickly and accurately. The company claims its fall detection algorithm offers 99.5 % accuracy, allowing seniors to maintain independence while ensuring caregivers are notified in real time. The system supports anonymized, blurred video snippets and captures footage only when an incident occurs, aligning with privacy requirements. For senior living communities, commercial solutions like KamiCare offer enterprise versions of fall‑detection cameras and 24/7 professional monitoring.
Demand for AI‑powered cameras is surging. An industry report from Global Market Insights notes that the AI camera market was valued at USD 7.55 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 18 % between 2024 and 2032. Growth is driven by improvements in machine‑learning algorithms that enable real‑time object detection, facial recognition and behaviour analysis. However, the report warns that data privacy and security are significant challenges: continuous video collection raises concerns about unauthorized access, data breaches and misuse of sensitive information. Organisations implementing AI cameras must therefore invest in robust encryption, comply with regulations and be transparent about data handling.
AI camera technology will continue to evolve. Advances in deep learning, edge computing and digital twin technology will allow camera systems to predict problems before they occur. In the LookDeep study, real‑time alerts not only signalled immediate risks but also provided population‑level trends to inform staffing and clinical pathways. Future AI cameras may integrate vital‑sign sensors and electronic health records to anticipate sepsis, track medication compliance and personalize rehabilitation plans. Computer‑vision pipelines will incorporate transformer‑based models and temporal analysis to detect subtle anomalies.
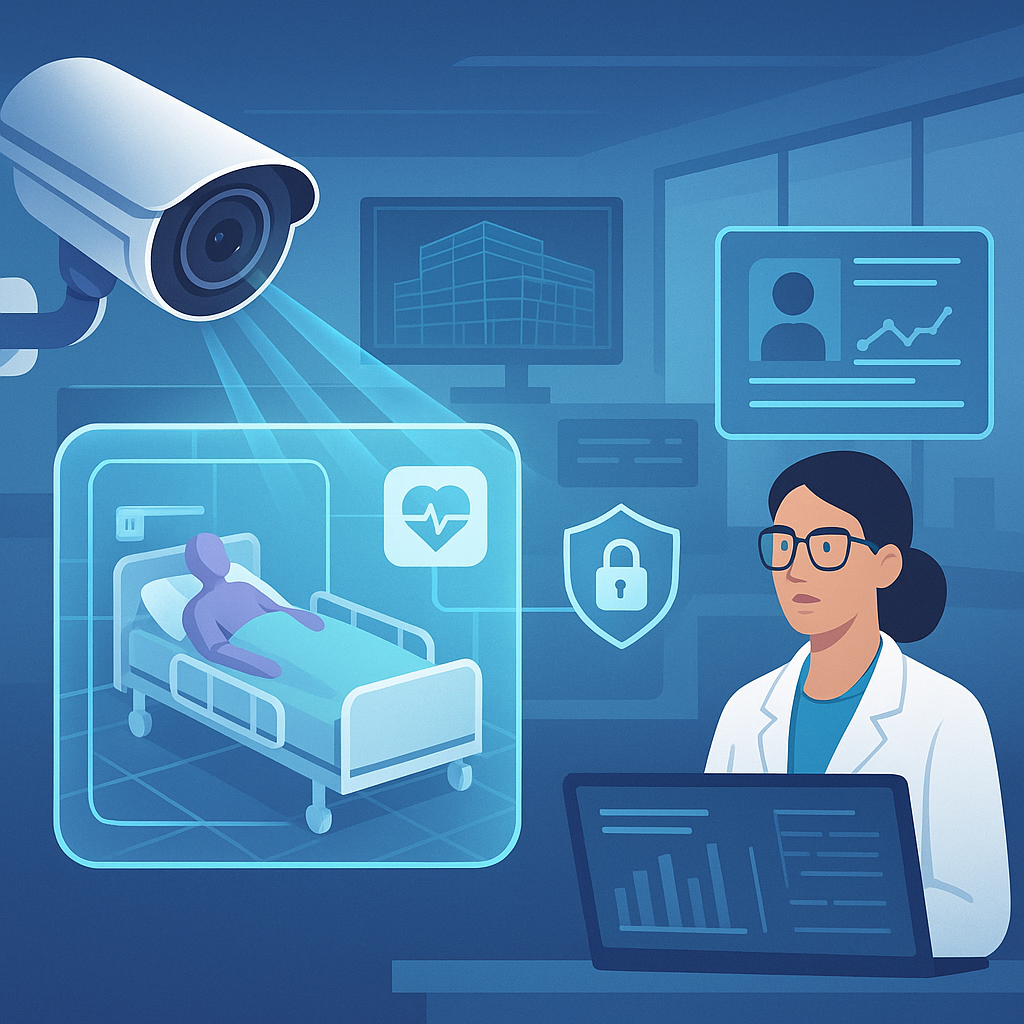

AI cameras raise questions about privacy, consent and trust. To maintain patient confidence, hospitals must adopt privacy‑preserving techniques such as face‑blurring, anonymization and on‑device processing. Industry guidelines like the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) provide a framework, but ongoing collaboration with ethicists and patient advocates is essential. As CHIME’s resource post notes, vision‑AI systems should anonymize data whenever possible and store footage only when necessary, and cybersecurity must be a priority. Edges devices and privacy‑preserving algorithms can minimize data transfer and reduce the risk of breaches.
The next generation of AI cameras will work alongside other Internet of Things (IoT) devices and digital twins. A digital twin is a virtual representation of a physical asset that streams real‑time sensor data to model behaviour and predict failures. By integrating AI camera feeds with digital twins of hospital rooms, corridors or entire facilities, healthcare providers can simulate scenarios, optimize workflows and respond proactively. This holistic approach ensures that safety, efficiency and comfort are considered together.
AI camera monitoring does not eliminate the need for human caregivers; instead, it reallocates tasks. Automation of routine observation allows nurses and security staff to focus on complex decision‑making, emotional support and high‑risk interventions. Hospitals adopting AI cameras should invest in workforce reskilling and partner with business culture coaches to ensure that technological change aligns with organizational values.
IronHive.ai offers a comprehensive platform that combines AI camera monitoring with digital twin technology, workflow automation and compliance tools. Its AI Agents integrate with existing systems across finance, HR, operations and IT to automate workflows and deliver insights ironhive.ai. Key features relevant to healthcare include:
IronHive’s agents monitor cameras and other sensors, automatically route exceptions to human decision‑makers and triage tickets ironhive.ai. This reduces response times and prevents adverse events.
The platform conducts real‑time compliance checks, flags vendor risk and logs every action for audit purposes ironhive.ai. This is critical when deploying camera systems in regulated environments such as hospitals and senior care facilities.
IronHive builds digital replicas of physical assets (buildings, equipment, even entire facilities) and overlays them with AI‑driven insights. Combined with smart camera monitoring, this allows organizations to identify anomalies or threats before they manifest, support predictive maintenance and optimize resource allocation IronHive.ai
Although not explicitly quoted, IronHive emphasizes data security and privacy, aligning with HIPAA and GDPR requirements through encryption and anonymization.
By offering customized deployments and a business culture coach to facilitate change management, IronHive ensures that technological innovation aligns with each client’s culture. Its scalability and focus on return on investment make it suitable for healthcare networks of all sizes.
AI camera monitoring has evolved from watchtowers and analog CCTV systems into a sophisticated tool that can detect falls, flag anomalies and even predict adverse events. In hospitals and senior care facilities, these systems improve patient safety, reduce workload, enhance operational efficiency and support data‑driven decision‑making. However, growth in AI camera adoption comes with concerns about privacy, data security and ethical deployment. The best solutions employ anonymization, comply with regulations and integrate with broader digital strategies.
IronHive.ai exemplifies this holistic approach, combining AI‑powered camera monitoring with digital twins, workflow automation, compliance tools and cultural support. For healthcare executives seeking to enhance safety and efficiency while maintaining trust, adopting such a comprehensive platform can turn cameras from passive observers into proactive partners in care.
© IronHive.AI, All Rights Reserved.